1.物以类聚,人以群分。出处:《周易•系辞》 说明好人会因兴趣相同而聚集在一起;坏人则因利益而彼此匀结。
2.星星之火,可以燎原。出处:《尚书•盘庚 上》含义:比喻人们要注意小过错,否则将演变成大祸。
3.千里之行,始于足下。出处:李耳《 老子•六十四章 》含义:说明在做每一件事时,都要下定决心去做,才能达到目标。
4.自知不自见,自爱不自贵。出处:李耳《老子•七十二章》 含义:劝戒世人要了解自己的能力而不急于表现自我;要能自爱,也能谦虚、不骄傲。
5.信言不美,美言不信。出处:李耳《老子•八十一章》含义:劝人不要听信甜言蜜语,要懂得明辫真实的话。
6.工欲善其事,必先利其器。出处:《论语•卫灵公》 含义:说明要把事情办好,就必须事先做好准备功夫。
7.小不忍则乱大谋。出处:《论语•卫灵公》含义:劝勉世人办事要沉得住气,能忍让,以免因小失大。
8.知彼知己,百战不殆。出处:孙武《孙子•谋攻篇》含义:在面对竞争时须清楚了解自己与对方的情况,这样才能无往不利,打败对方。
9.老吾老以及人之老,幼吾幼以及人之幼。出处:孟柯《孟子•梁惠王上》含义:勉励世人发扬博爱的精神,敬老爱幼。
10.尺有所短,寸有所长;物有所不足,智有所不明。出处:屈原《卜居》含义:说明任何事物都各有长短,各有利弊。
11.泰山不让土壤,故能成其大。出处:李斯《谏逐客书》含义:比喻要接纳各方面的人才,才能壮大阵容。也指要吸收各方面的知识,才能使学识渊博。
12.临河而羡鱼,不如归家织网。出处:刘安朝代《淮南子•说林训》含义:说明要达成愿望,惟有靠实际的行动。
13.差之毫厘,缪以千里。出处:戴圣《礼记•经解》含义:强调凡事须小心处理,因为小小的差失最终会造成很大的错误。
14.士别三日,即更刮目相待。出处:陈寿《三国志•吴书•吕蒙传》含义:形容人时时刻刻都在进步和改变,所以不能以旧的眼光来评定一个人。
15.不人虎穴,焉得虎子。出处:范哗《后汉书•班超传》含义:比喻不冒险行事,不经历艰险,就无法获得成功。例句:所谓不人虎穴,焉得虎子,你做事这样畏首畏尾,不敢冒险,哪能成功?
16.城门失火,殃及池鱼。出处:杜弼《为东魏檄梁文 》含义:比喻无辜者被牵连而受害。
17.积财千万,不如薄伎在身。出处:颜之推《颜氏家训•勉学》含义:劝勉世人须掌握个人谋生的技能,而不是依靠父母的家财。
18.健儿须快马,快马须健儿。出处:乐府民歌《折杨柳歌 》含义:比喻有才能的人须要搭配良好的环境和设备,才能有出色的表现。
19.射人先射马,擒贼先擒王。出处:杜甫《前出塞诗》之六含义:比喻找人要找首领,处理事情则要从关键下手。
20.朱门酒肉臭,路有冻死骨。出处:杜甫《自京赴奉先县咏怀五百字》含义:反映社会上贫富悬殊的不合理现象。
21.读书破万卷,下笔如有神。出处:杜甫《奉赠韦左垂丈二十二韵》含义:说明多读书,把书读熟、读通,写作能力自然而然会提高,写出好文章。
22.黑发不知勤学早,白首方悔读书迟。出处:颜真卿《劝学》含义:警戒人们要趁年轻时勤奋读书,以免老来后悔。
23.野火烧不尽,春风吹又生。出处:白居易《赋得古原草送别》含义:比喻无法彻底清除恶势力,一有机会,它就会卷土重来。
24.春种一粒粟,秋收万颗子。出处:李绅《悯农二首》含义:说明只要工作勤奋,就能有好的成果。
25.劝君莫惜金缕衣,劝君惜取少年时。出处:杜秋娘《金缕衣》含义:劝勉人们珍惜宝贵的少年时光,勤奋求上进。
26.远上寒山石径斜,白云生处有人家。出处:杜牧《山行》含义:描绘山间秋天的景色,展现一幅动人的秋色之图。
27.一人传虚,万人传实。出处:道原《景德传灯录》含义:说明谣言的可怕,我们须特别小心。
28.出淤泥而不染。出处:周敦颐《爱莲说》含义:比喻品德高尚、洁身自爱的人,纵使身处恶劣的环境也不会受其影响。
29.由俭人奢易,由奢人俭难。出处:司马光《训俭示康》含义:劝告人们远离奢侈的生活,时时养成节俭的好习惯。
30.负岌从师,不远千里。出处:司马光《资治通鉴•汉纪四十三•顺帝永建二年》含义:说明有求知欲的人,不畏惧路途有多遥远,都会去向名师求取学问。
31. 知己之短,不掩人之长。出处:司马光《资治通鉴•梁纪七•武帝大通元年》含义:劝勉人要知道自己的缺点,也要欣赏别人的优点,从而学习别人的优点来纠正自己的缺点,以提升自己。
32.物极则反,器满则倾出处:司马光《资治通鉴•唐则天后长安二年》含义:劝戒我们不管做什么事,都要适可而止,不要太过分,否则就会产生反效果。
33.莫等闲、白了少年头,空悲切。出处:岳飞《满江红》含义:劝勉人们要珍惜少年的时光,及时努力求上进,以免年老时后悔。
34.水清出石鱼可数,林深无人鸟相呼。出处:苏轼《腊日游孤山访惠勤惠思二僧》含义:形容山林溪流幽静美丽,极具大自然之美。
35.纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行。出处:陆游《冬夜读书示子聿》含义:说明只有亲自去实行,才能把知识掌握得好。
36.犬守夜,鸡司晨,苟不学,曷为人。出处:王应麟《三字经》含义:说明万物有各自担任的职务。劝勉一个人要勤于学习,才能做好自己份内的工作。
37.从来好事天生俭,自古瓜儿苦后甜。出处:白朴《喜春来•题情》含义:说明在通拄理想的路程上都会遇到挫折,必须经过一番的努力奋斗才能实现。
38.金玉其外,败絮其中。出处:刘基《卖柑者言》含义:比喻外表完美,可是里头破败,即虚有其表。
39.万事俱备,只欠东风。出处:罗贯中《三国演义》含义:说明一切已准备好,就只是欠缺一样关键性的东西,而使整个计划不能按时进行。
40.蜀中无大将,廖化作先锋。出处:壮者 《扫迷帚》含义:比喻没有特出的人才,只好由平庸的人出任要职。
1)君子绝交,不出恶声
出处:<战国策。燕策>
作者:不详(西汉刘向所辑)
朝代:战国时代
语译:有修养的人与人之间断绝来往的时候,是不会说不好听的话的。意思:说明品格高尚的人与人之间绝交是经过一番深思熟虑之后才决定的,因此不会怀恨在心,事后仍然会与对方保持一贯的君子风度。
2)祸莫大于不知足
出处:<老子。四十六章>
作者:老子(李耳)
朝代:春秋时代
语译:祸患的原因,起于人不知道满足。意思:说明人的贪念及不知满足的心理会引起战争等祸患
3)不经一事,不长一智
出处:<红楼梦。第六十回>
作者:曹雪芹朝代:清朝
语译:不经历一件事情,就不会增长一点知识。
意思:比喻世人要多经阅历,才能增加知识
4)三人行,必有我师焉
出处:<论语。述而>
作者:孔子的弟子所编
朝代:战国时代
语译:几个人在一起上路,其中必定有一个可以成为我的老师。意思:劝勉世人要虚心向人学习,好以人为师
5)劝君莫打枝头鸟,子在巢中望母归
出处:<鸟>
作者:白居易
朝代:唐朝
语译:劝你不要打枝头上的鸟儿,鸟儿在巢中正盼望着母鸟回来意思:强调人人应有慈悲怜悯之心,而伤害别人的念头千万不可以有,以免后患无穷。
6)己所不欲,勿施于人
出处:<论语。颜渊>
作者:孔子的弟子所编
朝代:战国时代
语译:自己所不喜欢的东西,不要把他推给别人意思:做人要处处为他人着想,自己不愿意接受的,不要强加在他人身上
7)亡羊而补牢,未为迟也
出处:<战国策。楚策四>
作者:不详(西汉刘向所辑)
朝代:战国时代
语译:羊儿因羊圈破了而套走了,若能立刻修补围栏,也不算太迟意思:比喻事情出了差错,及时设法补救还来的及
8)业精于勤,荒于嬉
出处:<进学解>
作者:韩愈
朝代:唐朝
语译:学业因勤勉变得高深,嬉戏则会荒废学业意思:劝勉人们勤奋向学,不可贪玩而荒废了学业
9)一日不见,如三秋兮
出处:<诗经。王风。采葛>
作者:不详
朝代:周初至春秋时代
语译:一天见不到你,就很象隔了三年般长久意思:形容对心上人的强烈思念之情
10)投我以桃,抱之以李
出处:<诗经。大雅。仰>
作者:不详
朝代:周初至春秋时代
语译:别人送我桃子,我报答他李子意思:人与人之间应该礼尚往来。
11)小时了了,大未必佳
出处:<世说新语。言语>
作者:刘义庆
朝代:南朝宋代
语译:小时候聪明,长大后未必聪明意思:比喻小时候聪明的人,也需要后天的栽培,否则长大后未必聪明。
12)一语为重百金轻
出处:<商映诗>
作者:王安石
朝代:北宋
语译:一句话比百两黄金还重要意思:做人应守诺言,言出必行
13)近朱者赤,近墨者黑
出处:<太子少傅箴>
作者:傅玄
朝代:晋代
语译:多接近红色就容易被红色所沾染而变红,多接近黑色就容易被黑色所沾染而变黑意思:比喻接近好人使人变好,接近坏人使人变坏
14)记人之善,忘人之过
出处:<三国志>
作者:陈寿
朝代:晋代
语译:记取别人的优点,忘记别人的过错意思:劝人不要记过,应以宽阔的胸怀待人
15)敏而好学,不耻下问
出处:<论语。公治长>
作者:孔子的弟子所编
朝代:战国时代
语译:天资聪颖又好学习,即使向地位,学问比自己低的人请教也不觉得羞耻意思:劝勉世人应谦虚好学,不以地位,学问比自己低的人请教而感到羞耻
16)温故而知新,可以为师也
出处:<论语。为政>
作者:孔子的弟子所编
朝代:战国时代
语译:温习旧有的知识一了解新的知识,就能够成为老师。意思:强调已经学的知识必须经常温习,整理,同时不能忽视学习新知识。
17)本是同根生,相煎何太急
出处:<七步诗>
作者:曹植
朝代:魏朝
语译:原本是同一条根上生长出来的,又何必急于互相煎煮。意思:形容兄弟相残的丑恶行径
18)名不正,则言不顺
出处:<论语。子路>
作者:孔子的弟子所编
朝代:战国时代
语译:名份不正当,那么说话就无法理直气壮,做事时他人也不会服从。意思:名份不正,说话或做事就不能达到目的。
19)口惠而实不至
出处:<礼记。表记>
作者:戴圣
朝代:西汉
语译:在口头上答应给别人好处,但实际上没有行动以实现诺言。意思:批评那些随意许下诺言,却没有实现的人。
20)尽的大的责任,就得大快乐,尽的小的责任,就得小快乐。
出处:<最苦与最乐>
作者:梁启超
朝代:现代
语译:尽了最大的责任,就会得到很大的快乐,尽了较小的责任,就会得到较小的快乐。意思:劝勉世人做事应尽最大的责任,以便能得到最大的快乐
21)人固有一死,或重于泰山,或轻于鸿毛
出处:<<抱任安书>>
作者:司马迁
朝代:西汉
意思:热门必定要死的,但有人却死得有价值,比泰山还重,有人却死 有人却死得毫无意义。比雁儿的羽毛还轻。说明了死要 四得有价 值、有意义。
22)年年岁岁花相示,岁岁年年人不同。
出处:《代悲白头翁》
作者:刘希译
朝代:唐朝
意义:花开花谢,每一年的花儿都不一样,人却变化无穷。表示感慨青 春是很容易消逝。
23)一语为重百金轻
作者:王安石
朝代:北宋
意思:诺言比金钱重要。强调人们必须遵守诺言。
24)四海之内,皆兄弟也
作者:孔子之门人
朝代:春秋
意思:全世界应该不分彼此,要象兄弟般相亲相爱,互相爱护。
Press this!
Try and See how Good is Your Peribahasa
Simpulan Bahasa
1. Ada akal- mempunyai idea
2. Ada angin- orang yang mempunyai sikap yang berubah-ubah
3. Ada hati- ingin akan sesuatu
4. Ada domba- melaga-lagakan orang yang supaya berpecah belah
5. Air muka- rupa yang menggambarkan perasaan seseorang
Peribahasa
1. Bagai abu di atas tunggul- kedudukan yang tidak pasti
2. Seperti anai-anai bubus- suasana yang ramai dengan manusia
3. Seperti anak ayam kehilangan ibu- orang yang hilang tempat bergantung
4. Seperti anjing bercawat ekor- orang yang tidak mahu mengikut perubahan
5. Seperti anjing berebut tulang- orang yang tamat dalam perebutan harta
Perjanjian Aqabah
- Ditandatangani pada tahun 612M. antara orang Arab dengan Nabi Muhammad s.a.w..
- Perjanjian ini dikenali sebagai Perjanjian Aqabah Pertama.
- Suku Aus dan Khazjah hendaklah beriman kepada Allah dan Rasul.
- Satu lagi perjanjian antara Nabi Muhammad s.a.w. dengan suku Aus dan Khazjah ialah pada tahun 622M..
- Perjanjian ini dikenali sebagai Perjanjian Aqabah Kedua.
- Suku Aus dan Khazjah menjemput Nabi Muhammad s.a.w. dan orang Islam di Makkah berhijrah ke kota Makkah.
Piagam Madinah
- Merupakan seduah perlembagaan bertulis yang pertama dirangka di dunia.
- Menjadi asas negara berdaulat.
- Asas pemerintahan kerajaan Islam Madinah.
- Mencacatkan tentang peraturan, tanggungjawab ketua negara dan rakyatnya, serta berasakan persetujuan orang Islam dan orang bukan Islam.
- Nabi Muhammad s.a.w. dilantik sebagai pemimpin.
Hijrah
- Berasal daripada perkataan Arab yang bermaksud berpindah.
- Hijrah bermaksud perpindahan orang Islam dari Makkah ke Madinah.
- Orientalis Barat mentafsirkan hijrah sebagai suatu pelarian.
- Pernghijrahan adalah disebabkan perintah Allah melalui wahyu.
- Hijrah bertujuan untuk meneruskan penyebaran agama Islam.
- Menberi peluang kepada Nabi Muhammad s.a.w. untuk mendamaikan suku Arab di Madinah.
Penyerbaan Islam
- Menghantar perutusan ke rom, Rom Timur, Parsi, Mesir, dan wilayah di sekitar Semenanjung Tanah Arab.
- Pertempuran dan peperangan dalam Islam bertujuan menentang kezaliman dan menpertahankan diri.
- Contoh peperangan: Perang Badar, Perang Uhud, Perang Khandak, dan Perang Tabuk.
Perjanjian Hudaibiyah
- Orang Islam bercadsang untuk menziarahi Makkah pada tahun 628M..
- Orang Islam Quraisy di Hubaibiyah menyekat kedatangan orang Islam Madinah,
- Perjanjian Hudaibiyah termeterai antara Nabi Muhammad s.a.w. dengan Suhail bin Amru.
- Orang Islam berpeluang untuk menunaikan haji pada tahun 629M..
Pembukaan Semula Kota Makkah
- Kota Madinah ialah tempat kelahiran Nabi Muhammad s.a.w.
- Tempat lahirnya agama Islam.
- Empat pasukan tentera telah disediakan dan bergerak masuk ke kota Makkah menerusi empat arah yang berlainan.
- Kota Makkah ditawan semula pada tahun 630M..
Newton's First Law of Motion:I. Every object in a state of uniform motion tends to remain in that state of motion unless an external force is applied to it.This we recognize as essentially Galileo's concept of inertia, and this is often termed simply the "Law of Inertia".
Newton's Second Law of Motion:II. The relationship between an object's mass m, its acceleration a, and the applied force F is F = ma. Acceleration and force are vectors (as indicated by their symbols being displayed in slant bold font); in this law the direction of the force vector is the same as the direction of the acceleration vector. This is the most powerful of Newton's three Laws, because it allows quantitative calculations of dynamics: how do velocities change when forces are applied. Notice the fundamental difference between Newton's 2nd Law and the dynamics of Aristotle: according to Newton, a force causes only a change in velocity (an acceleration); it does not maintain the velocity as Aristotle held.
This is sometimes summarized by saying that under Newton, F = ma, but under Aristotle F = mv, where v is the velocity. Thus, according to Aristotle there is only a velocity if there is a force, but according to Newton an object with a certain velocity maintains that velocity unless a force acts on it to cause an acceleration (that is, a change in the velocity). As we have noted earlier in conjunction with the discussion of Galileo, Aristotle's view seems to be more in accord with common sense, but that is because of a failure to appreciate the role played by frictional forces. Once account is taken of all forces acting in a given situation it is the dynamics of Galileo and Newton, not of Aristotle, that are found to be in accord with the observations.
Newton's Third Law of Motion:III. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. This law is exemplified by what happens if we step off a boat onto the bank of a lake: as we move in the direction of the shore, the boat tends to move in the opposite direction (leaving us facedown in the water, if we aren't careful!).
Golongan Kata
1. Morfologi
# Kata tunggal- bunga, MARA- Majlis Amanah Rakyat
# Kata terbitan- di + saran
# Kata majmuk- kerja + sama = kerjasama
# Kata ganda - budak-budak, lelaki, saudara-mara
2. Kata nama
# Kata nama Am - guru, senyuman
# Kata nama Khas - Azri, Sang Kancil (hidup), Putrajaya (tidak hidup)
3. Kata ganti nama
# Kata ganti nama tunjuk- ini, itu
# Kata ganti nama diri - Pertama: aku,saya,hamba - Kedua: anda, saudara - Ketiga:dia, ia, nya
# Kata ganti nama tanya - apa, siapa, mana
# Kata ganti nama tempat- sana, sini, situ
# Kata ganti nama tak tentu - apa-apa, sesiapa, mana-mana
4.Kata kerja
# Kata kerja tak transitif(tidak memerlukan penyambut) - Berpelengkap: berbuat(tanpa pelengkap), berbuat jahat(pelengkap) -Tanpa pelengkap: beristihara, tersenyum
# Kata kerja transitif - membuka pintu
# Kata kerja pasif- Pertama: Gambar itu aku tulis - Kedua: Hendaklah kamu bersihkan bilik itu. - Ketiga: dipantau oleh -Awalan teR: Ali terlanggar oleh lori - Awalan beR: Seluar anaknya sudah berjahit, belum -Apitan ke...an-kecurian, kehujanan, kesiangan, kehausan -Dengan kata kena- kena tampar, kena ugut, kena tendang
5. Kata adjektif- canggih, jingga, singkat, bulat, lampau, jauh, selalu, geram, manis
6.Kata tugas
# Kata hubung - Kata hubung gabungan: maka, sambil(setara), bukan sahaja, tambahan pula(berpasangan) -Kata hubung pancangan: yang(relatif), bahawa. untuk(kompleme), hingga,apabila, sekiranya , setelah(keterangan)
# Kata seru - aduh, aduhai, ah, amboi, cis, eh, oh, wahai, wah
# Kata tanya-bila, berapa
# Kata perintah- jangan, usah(larangan), tolong(permintaan), jemput,sila(silaan), harap, minta(suruhan)
# Kata pembenar - betul, benar, ya
# Kata pangkal ayat - oleh itu, justeru, namun begitu
# Kata bantu - Kata bantu aspek: telah, sedang, akan, belum -Kata bantu ragam: heandak, dapat , mesti, mungkin
# Kata penegas - hadapan: terlalu, paling - belakang: sekali, benar, nian =Bebas- amat, sungguh
# Kata penegas- jua, juga,, hanya, pun, sahaja, lagi, memang -partikel penegas: -kah, -lah -tah
# Kata nafi- bukan, tidak
# Kata pemeri - ialah, adalah
# Kata sendi nama- di, ke, kepada, daripada, umpama, demi, sejak, oleh, hingga, dalam, antara
# Kata arah - sudut, selatan, tengah, samping, luar, sisi, penjuru, segi
# kata bilangan - tentu: dua puluh -tak tentu: sekalian, beberapa -himpunan: riduan, bertahun-tahun -pisahan: masing-masing, setiap - pecahan: suku, sebahagian, setengah -tingkat: pertama, kelapan
7.Pembentukan kata
#pengimbuhan- Awalan: pe-, peN-, peR-, ke-, se- -Awalan pinjaman: juru-, tata-, pra- eka-, maha-, dwi,panca-, sub- pro- auto- inter-, poli- anti- -Akhiran: -an -Akhirab pinjaman: -wan, -isme-, -si -tik, -wati -Apitan:pe...an, pemer...an -Sisipan:-an-, -el-, -er-
# Penggandaan- kata nama: kunang-kunang, mata-mata -kata kerja: pandang-pandang, cerai-berai - Kata adjektif: hijau-hijau, gundah-gulana
# Pemajmukan - Rangkai kata bebas: susu segar, air hujan -Istilah khusus: mata pelajaran, kertas kerja, hak milik -Kiasan(simpulan bahasa)- asam garam, makan hati
Frasa
-Sekurang-kurangnya satu atau dua perkataan
1. Frasa nama- Beliau guru
2. Frasa Kerja
# Frasa kerja tak transitif- Pengganas itu lari ke dalam hutan [pengganas itu= subjek, lari...=predikat]
# Frasa kata transitif- Pemburu itu menembak tupai itu dengan senapang.
3. Frasa Sendi: Adik saya tiggal di sini.
4. Frasa Adjektif: Cuaca itu ini sejuk banyak.
Klausa
1. Klausa subjek- Apa yang terjadi belum lagi diketahui.
2. Klausa predikat- Tiada seorang pun yang mahu menolongnya.
3. Klausa keterangan- Hujan turun dengan lebatnya sehingga seluruh kampung itu kebanjiran.
4. Klausa penerangan- Kagagalan dalam peperiksaan disebabkan oleh kenyataan bahawa dia malas belajar.
Klausa Utama- Kamu mesti belajat( Klausa utama) untuk mencapai kejayaan(klausa pengikutan).
Ayat
1. Ayat inti- Beliau ialah seorang guru.
2. Ayat penegas- Orang itu ialag pencuri
3. Ayat perbandingan- Ali sepandai Eng Soon.
4. Ayat Penggalan- Pergilah kau dari sini
5. Ayat tunggal- Saya makan nasi.
6. Ayat majmuk- dan, atau, lalu, maka, tetapi
7.Ayat songsang- Pelajar perempuan itu menangis -> Menangis pelajar perampuan itu.
世界上最远的距离 The most distant way in the world
不是生与死的距离 is not the way from birth to the end.
而是我站在你面前It is when I sit near you
你不知道我爱你 that you don't understand I love you.
世界上最远的距离 The most distant way in the world
不是我站在你面前 is not that you're not sure I love you.
你不知道我爱你 It is when my love is bewildering the soul
而是爱到痴迷 but I can't speak it out
却不能说我爱你 世界上最远的距离 The most distant way in the world
不是我不能说我爱你 is not that I can't say I love you.
而是想你痛彻心脾 It is after looking into my heart
却只能深埋心底 I can't change my love.
世界上最远的距离The most distant way in the world
不是我不能说我想你 is not that I'm loving you.
而是彼此相爱 It is in our love
却不能够在一起 we are keeping between the distance.
世界上最远的距离 The most distant way inthe world
不是彼此相爱 is not the distance across us.
却不能够在一起 It is when we're breaking through the way
而是明知道真爱无敌 we deny the existance of love.
却装作毫不在意 世界上最远的距离 So the most distant way in the world
不是树与树的距离 is not in two distant trees.
而是同根生长的树枝 It is the same rooted branches
却无法在风中相依 can't enjoy the co-existance.
世界上最远的距离 So the most distant way in the world
不是树枝无法相依 is not in the being sepearated branches.
而是相互了望的星星 It is in the blinking stars
却没有交汇的轨迹 they can't burn the light.
世界上最远的距离 So the most distant way in the world
不是星星之间的轨迹 is not the burning stars.
而是纵然轨迹交汇 It is after the light
却在转瞬间无处寻觅 they can't be seen from afar.
世界上最远的距离 So the most distant way in the world
不是瞬间便无处寻觅 is not the light that is fading away.
而是尚未相遇 It is the coincidence of us
便注定无法相聚 is not supposed for the love.
世界上最远的距离 So the most distant way in the world
是鱼与飞鸟的距离 is the love between the fish and bird.
一个在天 One is flying at the sky,
一个却深潜海底 the other is looking upon into the sea.
Domo (dohh-moh; Thank you or Hi!)
le (eee-eh; No or Don't mention it.)
Hai (hah-ee; Yes)
Wakarimasen (wah-kah-ree-mah-sen; I don't understand.)
Shiriiriasen (she-ree-mah-sen; I don't know the answer to that question.)
Zenzen (zehn-zehn; Not at all or It was nothing.)
Ii desu ne (ee-ee deh-soo neh; That's a great idea!)
Yatta(yaht-tah; Yahoo! I did it.)
Gambatte(gahm-baht-teh; Go for it! or Try your best!)
Omedeto (oh-meh-deh-tohh; Congratulations!)
Yokoso (yohh-koh-soh; Welcome!)
Shinpai shinaide (sheen-pah-ee shee-nah-ee-deh; Don't worry!)
Makasete (mah-kahTseh-teh; Count on me!)
So, so (sohh, sohh; You're right, you're right!) Used when you agree with someone's statement. This phrase is similar to what you mean when you say "yeah" in the middle of an English conversation just to let the other person know that you're listening.
Dame (dah-meh; You're not allowed to do that or That's bad!) Used when you want to stop someone from doing something or when you want to say that something is bad or impermissible. You'd never say this phrase to a superior or to someone older than you. You can say it to children, siblings, or very close friends.
Enryo shinaide (Don't be shy)
Japanese guests often refuse food or drink offers at least once. If you're the host, say enryo shinaide (ehn-ryoh shee-nah-ee-deh).
Mottainai (What a Waste/It's too qood)
Say mottainai (moht-tah-ee-nah-ee) to object to waste. You can also say it if someone lacks a true appreciation for something valuable.
Osakini (Pardon me, but I'm ieavinq now)
When you have to leave a gathering early, say osakini (oh-sah-kee-nee; literally means earlier) to display your thoughtfulness for others.
Sasuga (I'm impressed by you, as usual)
Sasuga (sah-soo-gah) literally means "as might have been expected," but it's commonly used as a compliment. If a friend wins a competition, say pasuga.
Gambatte (Try your best!)
The Japanese believe that the effort is more important than the result. If a friend's going to take an important exam, say gambatte (gahm-baht-teh) to her.
Shoganai (There's no choice/There's nothing that can be done)
When you're in a jam and none of the possible solutions will work well, choose one and say shoganai (shohh-gah-nah-ee), which shows that you've resigned yourself to the situation.
Okage-sama de (Luckily/Thanks to you)
If someone asks ogenki desu ka (oh-gehn-kee deh-soo kah; How are you?), answer with the modest okage-sama de (oh-kah-geh-sah-mah de) rather than genki desu (gehn-kee deh-soo; I'm fine). The original meaning is that your well-being is due to God and others, including the person you're talking to.
Gokuro-sama (Thank you for your trouble)
If you're the boss, say gokur5-sama (goh-koo-rohh-sah-mah) to each of your workers when they say good-bye to you at the end of the day.
yoroshiku (Pleased to meet you/1 appreciate your helping me)
You can say yoroshiku (yoh-roh-shee-koo) when you first meet someone, as in you're pleased to meet him. You can also say it after asking a favor of someone, in which case it means "I appreciate your helping me."
Taihen desu ne (That's tough)
Use this phrase to show sympathy, such as when your friend tells you about her difficulties.
Hello-KONNICHIWA
Good Morning-OHAYOUGOZAIMAS
Good Afternoon-KONNICHIWA
Good Evening-KONBANWA
Good Night-OYASUMINASAI
Good Bye-SAYOUNARA
Thank you-ARIGATOUGOZAIMAS
How are you doing?-GENKIDESKA?
I am fine. Thank you.-GENKIDES
I am hungry-ONAKA GA SUKIMASHITA
How do you do?-HAJIMEMASHITE
What is your name?-ONAMAEWA?
I, me, myself-WATASHI
am, are, is-DESU
you-ANATA
American (person)-AMERIKA-JIN
Japanese (person)-NIHON-JIN
college student-DAIGAKU-SEI
high school student-KOOKOO-SEI
My name is Katsumi-WATASHI WA KATSUMI TO IIMAS
Wife-TSUMA
Husband-OTTO
Son-MUSUKO
Daughter-MUSUME
Girl-friend / Boy-friend -KOIBITO
one-ICHI
two-NI
three-SAN
four-YON/SHI
five-go
six-roku
seven-NANA/SHICHI
eight-HACHI
nine-KYU/KU
ten-JU
白羊座 bai yang zuo おひつじ座 Aries
半人马座 ban ren ma zuo ケンタウルス座 Centaurus
宝瓶座 bao ping zuo みずがめ座 Aquarius
北冕座 bei mianzuo きたかんむり座 Corona Borealis
波江座 bo jiang zuo エリダヌス座 Eridanus
苍蝇座 cang ying zuo はえ座 Musca
豺狼座 chai lang zuo おおかみ座 Lupus
长蛇座 chang she zuo うみへび座 Hydra
船底座 chuan di zuo りゅうこつ座 Carina
船帆座 chuan fan zuo ほ座 Vela
船尾座 chuan wei zuo とも座 Puppis
大犬座 da quan zuo おおいぬ座 Canis Major
大熊座 da xiong zuo おおぐま座 Ursa Major
雕具座 diao ju zuo ちょうこくぐ座 Caelum
杜鹃座 du juan zuo きょしちょう座 Tucana
盾牌座 dun pai zuo たて座 Scutum
飞马座 fei ma zuo ペガサス座 Pegasus
飞鱼座 fei yu zuo とびうお座 Volans
凤凰座 feng huang zuo ほうおう座 Phoenix
海豚座 hai tun zuo いるか座 Delphinus
后发座 hou fa zuo かみのけ座 Coma Berenices
狐狸座 hu li zuo こぎつね座 Vulpecula
绘架座 hui jia zuo がか座 Pictor
唧筒座 ji tong zuo ポンプ座 Antlia
剑鱼座 jian yu zuo かじき座 Dorado
金牛座 jinniuzuo おうし座 Taurus
鲸鱼座 jing yu zuo くじら座 Cetus
巨爵座 jujuezuo コップ座 Crater
巨蛇座 ju she zuo へび座 Serpens
巨蟹座 ju xie zuo かに座 Cancer
矩尺座 ju chi zuo じょうぎ座 Norma
孔雀座 kong que zuo くじゃく座 Pavo
猎户座 lie hu zuo オリオン座 Orion
猎犬座 lie quan zuo りょうけん座 Canes Venaici
六分仪座 liu fen yi zuo ろくぶんぎ座 Sextans
鹿豹座 lu bao zuo きりん座? Camelopardalis
罗盘座 luo pan zuo らしんばん座 Pyxis
摩羯座 mo jie zuo やぎ座 Capricornus
牧夫座 mu fu zuo うしかい座 Bootes
南极座 nan ji zuo はちぶんぎ座 Octans
南冕座 nan mian zuo みなみのかんむり座 Corona Austrina
南三角座 nan san jiao zuo みなみのさんかく座 Triangulum Australe
南十字座 nan shi zi zuo みなみじゅうじ座 Crux
南鱼座 nan yu zuo みなみのうお座 Piscis Austrinus
麒麟座 qi lin zuo いっかくじゅう座? Monoceros
人马座 ren ma zuo いて座 Sagittarius
三角座 san jiao zuo さんかく座 Triangulum
山案座 shan an zuo テーブルさん座 Mensa
蛇夫座 she fu zuo へびつかい座 Ophiuchus
狮子座 shi zi zuo しし座 Leo
室女座 shi nv zuo おとめ座 Virgo
时钟座 shi zhong zuo とけい座 Horologium
双鱼座 shuang yu zuo うお座 Pisces
双子座 shuang zi zuo ふたご座 Gemini
水蛇座 shui she zuo みずへび座 Hydrus
天鹅座 tian e zuo はくちょう座 Cygnus
天鸽座 tian ge zuo はと座 Columba
天鹤座 tian he zuo つる座 Grus
天箭座 tian jian zuo や座 Sagitta
天龙座 tian long zuo りゅう座 Draco
天炉座 tian lu zuo ろ座 Fornax
天猫座 tian mao zuo やまねこ座 Lynx
天平座 tian ping zuo てんびん座 Libra
天琴座 tian qin zuo こと座 Lyra
天坛座 tian tan zuo さいだん座 Ara
天兔座 tian tu zuo うさぎ座 Lepus
天蝎座 tian xie zuo さそり座 Scorpius
天燕座 tian yan zuo ふうちょう座 Apus
天鹰座 tian ying zuo わし座 Aquila
天舟座 tian zhou zuo アルゴ座 Argo
网罟座 wang gu zuo レチクル座 Reticulum
望远镜座 wang yuan jing zuo ぼうえんきょう座 Telescopium
乌鸦座 wu ya zuo からす座 Corvus 武仙座 wu xian zuo ヘルクレス座 Hercules
仙后座 xian hou zuo カシオペヤ座 Cassiopeia
仙女座 xian nv zuo アンドロメダ座 Andromeda
仙王座 xian wang zuo ケフェウス座 Cepheus
显微镜座 xian wei jing zuo けんびきょう座 Microscopium
小马座 xiao ma zuo こうま座 Equuleus
小犬座 xiao quan zuo こいぬ座 Canis Minor
小狮座 xiao shi zuo こじし座 Leo Minor
小熊座 xiao xiong zuo こぐま座 Ursa Minor
蝎虎座 xie hu zuo とかげ座 Lacerta
虫偃 蜓座 yan ting zuo カメレオン座 Chamaeleon
英仙座 ying xian zuo ペルレオン座
Perseus 印第安座 yin di an zuo インデアン座 Indus
玉夫座 yu fu zuo ちょうこくしつ座 Sculptor
御夫座 yu fu zuo ぎょしゃ座 Auriga
圆规座 yuan gui zuo コンパス座 Circinus
天猫座 tian mao zuo やまねこ座 Lynx
Group 1 elements- Alkali metals:
Lithium(Li) Sodium(Na) Potassium(K) Rubidium(Rb) Caesium(Cs) Francium(Fr)
~All alkali metals are silver-colored, soft, low density metals, high electropositivity, good conductors of heat and electricity.
Atomic Size -increases gradually
Reason: The number of shells occupied with electron increases.
Density -increases gradually
----------Float on wate---------I--------Sink in water------------
Reason: The increase in atomic mass is bigger than the increase in volume.
Boiling and melting points -decreases gradually
Reason: As the atomic size increases, the metallic bonding between the atoms of alkali metals becomes weaker. Hence, less heat energy is required to overcome the weaker metallic bonding during melting or boiling.
Hardness -softer
Reactivity -increases
Reason: As the atomic size increases, the single valence electron becomes futher away from the nucleus. This causes the single valence electron can to be more weakly pulled by the nucleus. Thus, the single valence electron can be release more easily to achieve a stable electron arrangement.
Electropositivity -increases
Reactions of alkali metals with water:
Alkali metal + water → Alkali metal hydroxide + hydrogen gas
Example:
2K (s) + 2H2O (l) → 2KOH (aq) + H2 (g)
Reactions of alkali metals with oxygen:
Alkali metal + oxygen → Alkali metal oxide
Example:
4K (s) + O2 (g) → 2KO2H (s)
Reactions of alkali metals with chlorine and bromine:
Alkali metal + chlorine → Alkali metal chloride
Example:
2K (s) +Cl2 (g) → 2KCl (s)
Alkali metal + bromine → Alkali metal bromide
Example:
2K (s) +Br2 (g) → 2KBr (s)
Group 2 elements- Alkali earth metals:
Beryllium (Be) Magnesium (Mg) Calcium (Ca) Strontium (Sr) Barium (Ba) Radium (Ra)
The alkaline earth metals are silvery colored, soft, low density metals, which react readily with halogens to form ionic salts, and with water, though not as rapidly as the alkali metals, to form strongly alkaline (basic) hydroxides. For example, where sodium and potassium react with water at room temperature, magnesium reacts only with steam and calcium with hot water:
Mg + 2H2O → Mg(OH) 2 + H2
Beryllium is an exception: It does not react with water or steam, and its halides are covalent.
All the alkaline earth metals have two electrons in their outermost shell, so the energetically preferred state of achieving a filled electron shell is to lose two electrons to form doubly charged positive ions.
Group 3 to group 12 elements- Transition metals:
There are several common characteristic properties of transition elements:
They often form colored compounds.
Example:
Compound of transition elements Colour
Cobalt chloride crystal Pink
Copper(II) sulphate crystal Blue
Iron(II) sulphate crystal Pale yellow
Iron(III) sulphate crystal Brown
They can have a variety of different oxidation states.
Example:
Transition metals Oxidation number in compounds
Iron +2, +3
Nickel +2, +3
Copper +1, +2
Manganese +2, +3, +4 , +6, +7
Chromium +2, +3,
At least one of their compounds has an incomplete d-electron subshell.
They are often good catalysts.
Example:
Nickel acts as catalyst in the hydrogenation of alkene to form the corresponding alkane.
Cn H2n+H2--Ni→ Cn H2n+2
They are silvery-blue at room temperature (except copper and gold).
They are solids at room temperature (except mercury).
They form complex ions (aqua ones included).
Example:
Tetraamminecopper(II) ion,[Cu(NH3)4]2+
They are often paramagnetic.
Poor metals
The trivial name poor metals (or post-transition metals) is sometimes applied to the metallic elements in the p-block of the periodic table. Their melting and boiling points are generally lower than those of the transition metals and their electronegativity higher, and they are also softer. They are distinguished from the metalloids, however, by their significantly-greater boiling points in the same row.
"Poor metals" is not a rigorous IUPAC-approved nomenclature, but the grouping is generally taken to include aluminium, gallium, indium, tin, thallium, lead and bismuth; germanium, antimony and polonium are occasionally included, although these are usually considered to be metalloids or "semi-metals". Elements 113 to 116, which are currently allocated the systematic names ununtrium, ununquadium, ununpentium and ununhexium, would likely exhibit properties characteristic of poor metals; however as yet insufficient quantities of them have been synthesized to examine their chemical properties.
Nonmetals
The nonmetals are generally to:
Hydrogen (H)
In Group 14: Carbon (C)
In Group 15 (the pnictogens): Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P)
Several elements in Group 16, the chalcogens: Oxygen (O), Sulfur (S), Selenium (Se)
All elements in Group 17 - the halogens
All elements in Group 18 - the noble gases
Common properties considered characteristic of a nonmetal include:
poor conductors of heat and electricity when compared to metals
they form acidic oxides (whereas metals generally form basic oxides)
in solid form, they are dull and brittle, rather than metals which are lustrous, ductile or malleable
usually have lower densities than metals
they have significantly lower melting points and boiling points than metals
non-metals have high electronegativity
Semi-metals- Metalloids
There is no rigorous definition of the term, however the following properties are usually considered characteristic of metalloids:
metalloids often form amphoteric oxides.
metalloids often behave as semiconductors (B,Si,Ge) to semimetals (eg. Sb).
The concepts of metalloid and semiconductor should not be confused. Metalloid refers to the properties of certain elements in relation to the periodic table. Semiconductor refers to the physical properties of materials (including alloys, compounds) and there is only partial overlap between the two.
Some allotropes of elements exhibit more pronounced metal, metalloid or non-metal behavior than others. For example, for the element carbon, its diamond allotrope is clearly non-metallic, however the graphite allotrope displays limited electric conductivity more characteristic of a metalloid. Phosphorus, tin, selenium and bismuth also have allotropes which display borderline behavior.
In the standard layout of the periodic table, metalloids occur along the diagonal line through the p block from boron to astatine. Elements to the upper right of this line display increasing nonmetallic behaviour; elements to the lower left display increasing metallic behaviour. This line is called the "stair-step" or "staircase." The poor metals are to the left and down and the nonmetals are to the right and up. In addition, the halogens are found at the bottom right.
Lanthanides and actinides
The chemical properties of the lanthanides (elements 57-71) and the actinides (elements 89-103) are even more similar to each other than the transition metals, and separating a mixture of these can be very difficult. This is important in the chemical purification of uranium concerning nuclear power.
Group 17 elements- Halogens
Fluorine(F) Chlorine(Cl) Bromine(Br) Iodine(I) Astatine(At)
~Halogens exist as diatomic molecules, low density, high electronegativity, good oxidising agents, weak conductors of heat and cannot conduct electricity.
Atomic Size -increases gradually
Reason: The number of shells occupied with electron increases.
Density -increases gradually
Reason: The increase in atomic mass is bigger than the increase in volume.
Boiling and melting points -increases gradually
Reason: As the molecular size increases, the force of attraction(van der Waals forces) become stronger. Consequently, more heat energy is required to overcome the stronger of attraction during melting or boiling.
Colour -Pale yellow-----Greenish-yellow-----Reddish-brown------purplish-black
Reactivity -decreases
Reason: As the atomic size increases, the single valence electron becomes futher away from the nucleus. Therefore, the strength of the nucleus of a halogen atom to attract one more electron into the outermost shells to achieve an octet electron arrangement decreases.
Electronegativity -decreases
Reason: The number of shells occupied with electrons in the atom with halogens increases. This cause the outermost occupied shell to become further away from nucleus. Hence, the strength of the nucleus to attract outermost shell electrons becomes weaker.
Reactions of halogens with water:
Example:
Cl2 (g) + H2O (l) → HCl(aq) + HOCl (aq)
Chlorine Water Hydrochloric acid Hypochlorous acid
Reactions of halogens with iron:
Example:
2Fe(s) + 3Cl(g) → 2FeCl3 (s)
Iron Chlorine Iron(III) chloride
Reactions of chlorine with sodium hydroxide solution:
Example:
Cl2(g) + 2NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + NaCl(aq) + H2O
Chlorine Sodium hydroxide Sodium chloride Sodium chlorate Water
Group 18 elements- Noble gases:
Helium(He) Neon(Ne) Argon(Ar) Kryton(Kr) Xenon(Xe) Radon(Rn)
~All noble gases exist as single atom(monoatomic) which with a duplet and octet electron arrangement, colourless gases, insoluble in water, low density, weak conductors of heat and cannot conduct electricity.
Atomic Size -increases gradually
Reason: The number of shells occupied with electron increases.
Density -increases gradually
Reason: The increase in atomic mass is bigger than the increase in volume.
Boiling and melting points -increases gradually
Reason: As the molecular size increases, the force of attraction(van der Waals forces) become stronger. Consequently, more heat energy is required to overcome the stronger of attraction during melting or boiling.
1
Kepercayaan kepada tuhan
Keyakinan wujudnya Tuhan sebagai pencipta alam dan mematuhi segala suruhanNya berlandaskan pegangan agama masing-masing selaras dengan prinsip Rukun Negara
2
Amanah
Sikap bertanggungjawab yang boleh menimbulkan kepercayaan dan keyakinan orang lain
3
Harga diri
Keupayaan dan keyakinan diri agar mampu memulia dan menjaga maruah diri dalam kehidupan
4
Bertanggungjawab
Kesanggupan diri seseorang untuk memikul dan melaksanakan tugas serta kewajipan dengan sempurna
5
Hemah tinggi
Beradab sopan dan berbudi pekerti mulia dalam pergaulan seharian
6
Tolenrasi
Kesanggupan bertolak ansur, sabar dan mengawal diri bagi mengelakkan berlakunya pertelingkahan dan perselisihan faham demi kesejahteraan hidup
7
Berdikari
Kebolehan dan kesanggupan melakukan sesuatu tanpa bergantung kepada orang lain
8
Kerajinan
Usaha yang berterusan penuh dangan semangat ketekunan, kecekalan, kegigihan, dedikasi dan berdaya maju dalam melakukan sesuatu perkara
9
Kasih sayang
Kepekaan dan perasaan cinta yang mendalam serta berkekalan yang lahir daripada hati yang ikhlas
10
Keadilan
Tindakan dan keputusan yang saksama serta tidak berat sebelah
11
Rasional
Boleh berfikir berdasarkan alasan dan buktl yang nyata dan dapat mengambil tindakan berasaskan pertimbangan yang wajar
12
Kesederhanaan
Bersikap tidak keterlaluan dalam membuat pertimbangan dan tindakan sama ada dalam pemikiran, pertuturan atau perlakuan tanpa mengabaikan kepentingan diri dan orang lain
13
Kasih sayang terhadap keluarga
Perasaan cinta, kasih dan sayang yang mendalam dan berkekalan terhadap keluarga
14
Hormat dan taat kepada anggota keluarga
Memuliakan setiap anggota keluarga dengan berinteraksi dan menberi layanan secara bersopan untuk mewujudkan keluarga yang harmoni
15
Mengekalkan tradisi kekeluargaan
Menerima, menghormati dan mengamaikan sesuatu kebiasaan, adat dan kepercayaan yang diwarisi secara turun temurun dalam keluarga
16
Tanggungjawab terhadap keluaga
Kewajipan yang harus dilaksanakan oleh setiap individu terhadap keluarga untuk melahirkan keluarga bahagia, meningkatkan imej dan menjaga maruah keluarga
17
Menyayangi dan menghargai alam sekitar
Kesedaran tentang perlunya memelihara dan memulihara alam sekeliling untuk mengekalkan keseimbangan ekosistem
18
Keharmonian antara manusia dengan alam sekitar
Keadaan saling memerlukan hubungan yang harmoni antara manusia dengan alam sekeliling supaya kualiti kehidupan manusia dan alam sekeliling terpelihara
19
Kemapanan alam sekitar
Pengekalan keseimbangan alam sekeliling sebagai tanggungjawab bersama untuk kesejahteraan hidup
20
Peka terhadap isu-isu alam sekitar
Prihatin terhadap persoalan yang berkaitan dengan alam sekeliling dan berusaha menyelesaikannya
21
Cinta akan Negara
Perasaan sayang dan bangga kepada negara serta meletakkan kepentingan negara melebihi kepentingan diri
22
Taat dan setia kepada Raja dan Negara
Kepatuhan dan kesetiaan yang berkekalan kepada Raja dan Negara
23
Sanggup berkorban untuk negara
Kerelaan melakukan atau menyerahkan sesuatu termasuk nyawa sebagai tanda kebaktian untuk Negara
24
Melindungi hak kanak-kanak
Membela, memberi naungan dan memelihara hak kanak-kanak bagi menjamin kehiudupan mereka yang sempurna
25
Menhormati hak wanita
Melindungi dan mengiktirafkan wanita sebagai individu yang boleh memberi sumbangan dalam pembangunan keluarga, masyarakat, dan negara
26
Melindungi hak pekerja
Menghormati, menghargai, dan mengiktirafkan perkhidmatan, jasa, dan sumbangan dalam pembangunan negara
27
Menhormati hak golongan kurang berupaya
Memberi layanan secara bersopan kepada golongan kurang berupaya supaya tidak berasa tersisih dan mengiktirafkan mereka sebagai insan ciptaan tuhan
28
Melindungi hak pengguna
Membela dan memelihara hak individu untuk menjadi pengguna yang berilmu, mendapat perkhidmatan serta barangan yang berkualiti dan tidak mudah dieksplotasi
29
Mematuhi peraturan dan undang-undang
Menerima dan mematuhi peraturan dan undang-undang yang telah ditentukan tanpa mengira sesiapa dan di mana seseorang itu berada
30
Kebebasan bersuara
Kebebasan berucap dan mengeluarkan fikiran dengan batasan tertentu bagi menjaga keselamatan dan ketenteraman
31
Kebebasan beragamaan
Kebebasan setiap individu untuk menganut dan memelihara agamanya seperti yang diperuntukan dalam Perlembangan Malaysia
32
Penglibatan diri dalam pembangunan negara
Kebebasan untuk melibatkan diri dalam pelbagai aktiviti pembangunan negara dengan mematuhi peraturan, undang-undangan dan Perlembagaan Malaysia
33
Sikap keterbukaan
Bersedia memberi dan menerima pandangan, pembaharuan dan kritikan selaras dengan kebeneran fakta dan norma masyarakat
34
Hidup bersama secara aman
Hidup berbaik-baik antara satu sama lain dengan mengutamakan kedamaian dan keharmonian hidup tanpa mengira agama, bangsa dan budaya
35
Saling membantu dan bekerjasama
Usaha yang baik dan membina yang dilakukan bersama pada peringkat individu, komuniti atau negara untuk mencapai sesuatu matlamat
36
Saling menghormati antara negara
Menghargai dan memuliakan hubungan antara untuk menjamin kesejahteraan sejagat
Name: Jekyuen @Michelle
Email:jekyuen@hotmail.com
Birth:12th June 1991
Location:KL, Malaysia
HP. no.:016-######0
School:SSS
Tuition:Han Ling
Favourites:
-TVXQ, Super Junior,SS501, JJ, S.H.E.
-all colours
-water
-chocolate
-Mandarin, Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry
-story book,outer space
-playing computer,listening song,playing piano, karaoke,make friends
-doraemon
Dislike:
-busybody, 38, stingy,bother human
-Add math, History (so boring)
-drug
-durian
Contact:
HOTMAIL
Email:jekyuen@hotmail.com(add me if you know me)
Email:michelle_chang0612@hotmail.com9add me if you don't know me)
BLOG
http://jekyuen.blogspot.com
http://yuen91.blog.sohu.com
http://mcassiopeia.multiply.com
FRIENDSTER
http://www.friendster.com/mcassiopeia
http://www.friendster.com/jekyuen
Family: grandpa, grandma, mum, dad, brother, sister, more...
School classmates in 2007:rosemund,kha hoi,stephanie,audrey,yvonne,kah yerng,kar lin,min yee,simone(already changed class),faith,set wern,mee kuan,karen,jaren,yuen june,poi yen,
jiunn huah,kishan,yi fei,kong fai,choon yik,jun sheng,chan hui,chun yew,michael(taiwan exchange student
Now tition classmates:elaine,sherry,pik kuan,ellen(prawn
Other friends:choo ching,lee kuan,alvin,chia hong,mei yi,ai yuen,jia wen,yong da,more...
My teachers:da lao shi(wu xian jia
Horoscope: Gemini
Archives
-
▼
2007
(18)
-
►
September
(14)
- Sejarah-Form 4-Bab 5:Kerajaan Islam dii Madinah
- Newton's Law
- B.M.- Analisis Ayat
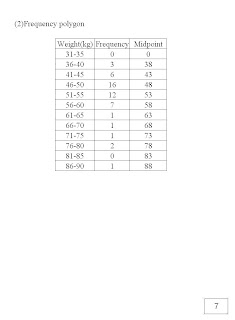
- Additional Mathematics Project Work 2007
- Click it!!
- 爱 love
- Japanese learning- Basic Phrases
- Japanese learning- Basic Vocabolary
- Japanese learning- Katakana
- Japanese learning- Hiragana
- Constellation
- Chemistry- Periodic table review
- Nilai P.Moral
- About me
-
►
September
(14)